If you’ve been following cryptocurrencies, or the banking and investing sectors, it’s likely you’ve come across the term ‘blockchain’. A relatively new addition to commercial vocabulary, the term blockchain has emerged as a result of technological advances and innovative methods of carrying out business.
Whilst the development and use of blockchain is still in its early stages, this unique technology has the capacity to disrupt industries, impact business processes and improve visibility to participants of a global supply chain.
What exactly is Blockchain?
So, what exactly is this blockchain concept we’ve been hearing so much about, how is it relevant to the supply chain and more importantly, what will its impact be?
To answer these questions, let’s start with the very basics – a definition of blockchain, its properties, aims and objectives and impact on supply chains. In our context, we’re talking about digital information (block) stored in a public database (the chain).
More about blocks
Blocks on the blockchain hold digital information and have three specific functions –
- to store information about a purchase – (For example, date, time and cost of your recent transaction)
- to store participants of a purchase – (For example, your name – but anonymously in the form of a digital signature or user name rather than true identity)
- blocks store information to distinguish them from other blocks. In much the same principle as us having Christian names, blocks have a unique code called a ‘hash’
One block on a blockchain can store up to 1MB of data – that’s easily a few hundred thousand transactions.

How does Blockchain work?
As its name suggests, a blockchain consists of multiple blocks strung together. For a block to be added to the chain, four things happen – a) a transaction – b) that transaction is verified, or confirmed, by computer, c) the transaction is stored in a block with others similar to it, and d), the block is then given its hash and added to the chain.
Is this information private or widely available?


Contents of blockchains can be viewed by anyone, but users can also opt to connect their computers to the blockchain network. This enables their computer to automatically update whenever a new block is added. Think of it in similar terms to a Facebook news feed updating when a new status is posted.
Security is assured by encryption technology using public and private keys – a public key, a randomly generated string of numbers, acts as the user’s address on the blockchain and the private key being the password which gives owners access to their digital assets.
So how does Blockchain technology disrupt industries?
The main difference and its disruptive element lies in trust being established through collaboration and code rather than a central authority. In reality, this means you no longer need a bank to transfer funds around the world. You no longer need a company or central authority to facilitate any form of transaction. Blockchain is revolutionary and has the potential to disrupt industries.
Can Blockchain technology add value for supply chains?
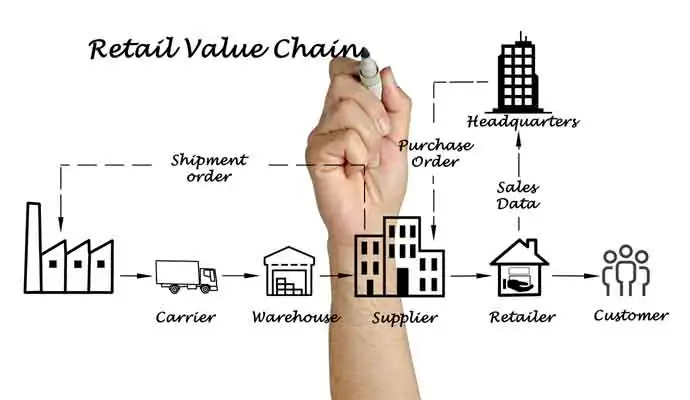
The advent of Blockchain technology has excited the IT and supply chain worlds and paved the way for innovative pilot projects. We believe the technology can add value for supply chains in a couple of basic ways:
- Replacing slow, manual processes
Although supply chains can handle large, complex data sets, many processes are still carried out using paper methods, which is time consuming and costly.
- Strengthening traceability
Increasing regulatory demand for ownership or custodial information is driving change. Improving traceability also adds value by mitigating against the high costs of quality issues such as recalls, reputational damage and loss of revenue from black market products.

Blockchain in action – pilot projects within supply chains
We’ve mentioned exciting pilot projects and initiatives, so let’s take a look at a few examples where leading players are beginning to put Blockchain into action.


- Walmart have tested an application tracing pork in China and produce in the US in order to authenticate transactions and accuracy and efficiency of record keeping
- IBM is working on cross-border, cross-party transactions using Blockchain technology to help improve processing efficiency
- BHP is introducing a Blockchain solution which replaces spreadsheets for tracking both internal and external samples from providers
- Following a successful pilot project tracing tuna in the South Asian supply chain, UK start-up, Provenance, has raised $800,000 to further adapt Blockchain technology in tracing food.

Advantages for the Transport & Logistics industry
At present the logistics industry has to deal with a range of frustrating issues which threaten cost efficiency. Misplaced packages, high volumes of administration, for example.
Imagine a system whereby as a package moves along its delivery route, it is recorded as a tamper proof transaction signed digitally by the carrier and vendor. Blockchain technology promises to hold this data in a secure manner, making it available from the chain from the perspective of each trading participant. The result is reduced quantities of paperwork, faster deliveries and increased profit.

The ability to link customer, order, carrier, payment and settlement information provides end consumers with real time views on delivery progress, delays and expected arrival times. End users will no longer be passed from pillar to post in telephone calls to try and locate goods, visibility will be open.
Blockchain technology also reduces the risk of fraud within the shipping industry. Automatic ID verification technology resolves any issues with ownership as possession of a package is tracked on the blockchain. ‘Smart’ contracts with global settlement and payment processes via Blockchain offer significant time and cost savings.


With the growth of e-commerce and last mile delivery inevitably linked, Blockchain has potential to eliminate the major obstacles plaguing the transportation and logistics industry. It’s an exciting, revolutionising and disrupting technology – and one we expect delivery companies to build solutions around and invest heavily in. Blockchain technology is here to stay and will continue to evolve to match the demands of the shipping industry. Watch this space!
